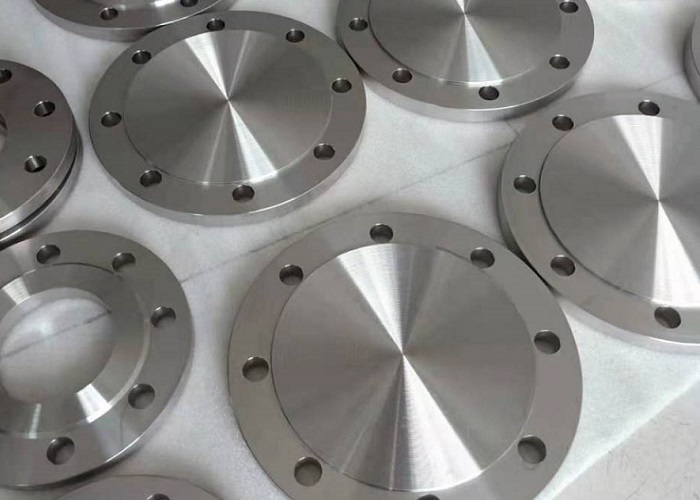
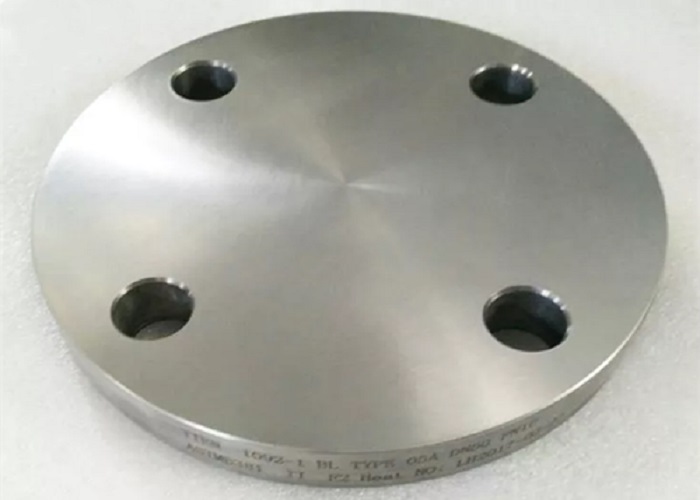
China Titanium Blind Flange manufacturer
ANSI B16.5 ASTM B381 Titanium Blind Flange
Specifications : ASTM B381 / ASME SB381
Standard : ANSI / ASME B16.5
Size : 1/8" NB to 48" NB
Pressure : 150#
Wall thickness: SCH5S-SCHXXS
Material: Titanium and titanium alloys
A titanium blind flange (BL flange) is a flange which has no bore, and is used to close ends of piping systems. A blind flange also permits easy access to a line once it has been sealed. The blind flanges are sometimes machined to accept a pipe of the nominal size to which reduction is being made. The reduction can be either threaded or welded. One of its functions is to block the end of the pipeline, and the other is to facilitate the removal of debris in the pipeline during maintenance. As far as plugging effect is concerned, it has the same effect as the head and cap. But the head can not be disassembled, and the blind flange is fixed by bolts, which is very convenient to disassemble.
Size: 1/2″ – 56″ (DN15 to DN1,400)
Pressure:
American standard series: CLASS 150, CLASS 300, CLASS 400, CLASS 600, CLASS 900, CLASS 1500, CLASS 2500
European standard series: PN 2.5, PN 6, PN 10, PN 16, PN 25, PN 40, PN 63, PN 100, PN 160, PN 250, PN 320, PN 400
Flange Facing Types: American series: Flat Face(FF), Raised Face(RF), Groove(G), Male and Female Face(MFM), Ring Type Joint (RTJ)
Material: Gr1 (3.7025), Gr2 (3.7035), Gr7 (3.7235), Gr12 (3.7105)
Normo:
GB/T9112-2000
GB/T9116 1-2000 GB/T9116 2-2000 GB/T9116 3-2000 GB/T9116 4-2000
GB/T9124-2000
SH/T3406-1996
GD2000 GD87-1101
HG/T20592-2009 HG/T20614-2009
HG/T20615-2009 HG/T20623-2009 HG/T20635-2009
ASME B16.5-2009
EN1092-1-2007 EN1759-1-2004
BS 1560-3 1-1989 BS 4504-3 1-1989
AFNOR NF E29-200-1-2007
ISO 7005-1-1992
AS2219-2000
JIS B2220-2004
China Titanium Blind Flange manufacturer Titanium information group supplies ANSI B16.5 ASTM B381 Titanium Blind Flange.
Blind flange dimensions are covered in ASME B16.5 – which covers Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings for size NPS ½” to 24” for above NPS 26” to 60” it should be as per ASME B16.47.
Class 150 Blind Flange Dimensions
Class 300 Blind Flange Dimensions
Class 400 Blind Flange Dimensions
Class 600 Blind Flange Dimensions
Class 900 Blind Flange Dimensions
Class 1500 Blind Flange Dimensions
Class 2500 Blind Flange Dimensions
Titanium Grade
Unua grado
is the most ductile and softest titanium alloy. It is a good solution for cold forming and corrosive environments. ASTM/ASME SB-265 provides the standards for commercially pure titanium sheet and plate.
Grade 2
Unalloyed titanium, standard oxygen.
Grade 2H
Unalloyed titanium (Grade 2 with 58 ksi minimum UTS).
3-a grado
Unalloyed titanium, medium oxygen.
Grades 1-4 are unalloyed and considered commercially pure or "CP". Generally the tensile and yield strength goes up with grade number for these "pure" grades. The difference in their physical properties is primarily due to the quantity of interstitial elements. They are used for corrosion resistance applications where cost, ease of fabrication, and welding are important.
Grade 5 also known as Ti6Al4V, Ti-6Al-4V or Ti 6-4
Klaso 6
contains 5% aluminium and 2.5% tin. It is also known as Ti-5Al-2.5Sn. This alloy is used in airframes and jet engines due to its good weldability, stability and strength at elevated temperatures.
Klaso 7
contains 0.12 to 0.25% palladium. This grade is similar to Grade 2. The small quantity of palladium added gives it enhanced crevice corrosion resistance at low temperatures and high pH.
Grade 7H
is identical to Grade 7 (Grade 7 with 58ksi minimum UTS).
9-a klaso
contains 3.0% aluminium and 2.5% vanadium. This grade is a compromise between the ease of welding and manufacturing of the "pure" grades and the high strength of Grade 5. It is commonly used in aircraft tubing for hydraulics and in athletic equipment.
Klaso 11
contains 0.12 to 0.25% palladium. This grade has enhanced corrosion resistance.
Grade 12
contains 0.3% molybdenum and 0.8% nickel. This alloy has excellent weldability.
Grades 13, 14, and 15
all contain 0.5% nickel and 0.05% ruthenium.
Grade 16
contains 0.04 to 0.08% palladium. This grade has enhanced corrosion resistance.
Grade 16H
is identical to Grade 16 (Grade 16 with 58ksi minimum UTS).
Grade 17
contains 0.04 to 0.08% palladium. This grade has enhanced corrosion resistance.
Grade 18
contains 3% aluminium, 2.5% vanadium and 0.04 to 0.08% palladium. This grade is identical to Grade 9 in terms of mechanical characteristics. The added palladium gives it increased corrosion resistance.
Grade 19
contains 3% aluminium, 8% vanadium, 6% chromium, 4% zirconium, and 4% molybdenum.
Grade 20
contains 3% aluminium, 8% vanadium, 6% chromium, 4% zirconium, 4% molybdenum and 0.04% to 0.08% palladium.
Grade 21
contains 15% molybdenum, 3% aluminium, 2.7% niobium, and 0.25% silicon.
Grade 23 also known as Ti-6Al-4V-ELI or TAV-ELI
Grade 24
contains 6% aluminium, 4% vanadium and 0.04% to 0.08% palladium.
Grade 25
contains 6% aluminium, 4% vanadium and 0.3% to 0.8% nickel and 0.04% to 0.08% palladium.
Grades 26, 26H, and 27
A hexagon formed from thermal stir welding of a Titanium alloy
all contain 0.08 to 0.14% ruthenium.
Grade 28
contains 3% aluminium, 2.5% vanadium and 0.08 to 0.14% ruthenium.
Grade 29
contains 6% aluminium, 4% vanadium and 0.08 to 0.14% ruthenium.
Grades 30 and 31
contain 0.3% cobalt and 0.05% palladium.
Grade 32
contains 5% aluminium, 1% tin, 1% zirconium, 1% vanadium, and 0.8% molybdenum.
Grades 33 and 34
contain 0.4% nickel, 0.015% palladium, 0.025% ruthenium, and 0.15% chromium. Both grades are identical but for minor difference in oxygen and nitrogen content.[30] These grades contain 6 to 25 times less palladium than Grade 7 and are thus less costly, but offer similar corrosion performance thanks to the added ruthenium.
Grade 35
contains 4.5% aluminium, 2% molybdenum, 1.6% vanadium, 0.5% iron, and 0.3% silicon.
Grade 36
contains 45% niobium.
Grade 37
contains 1.5% aluminium.
Grade 38
contains 4% aluminium, 2.5% vanadium, and 1.5% iron. This grade was developed in the 1990s for use as an armor plating. The iron reduces the amount of Vanadium needed as a beta stabilizer. Its mechanical properties are very similar to Grade 5, but has good cold workability similar to grade 9.